How to understand SCR conversion efficiency and SCR?
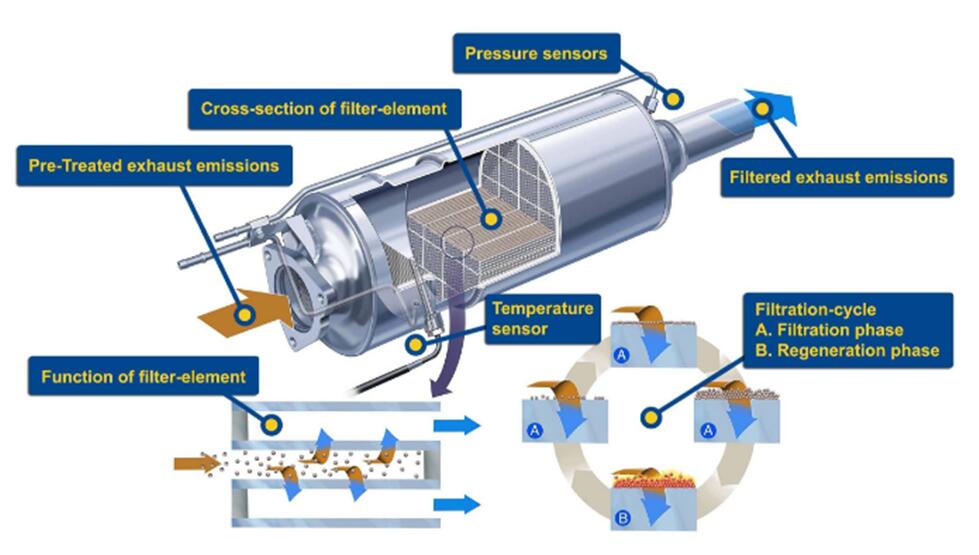
DPF process
1. SCR conversion efficiency: Under the action of SCR catalyst, nitrogen oxides undergo a chemical reaction with ammonia to convert into harmless components (nitrogen and water vapor).
2. SCR: Selective catalytic reduction reaction, which is not particularly unfamiliar to everyone. Here is a brief overview, and the working process is shown in the following figure
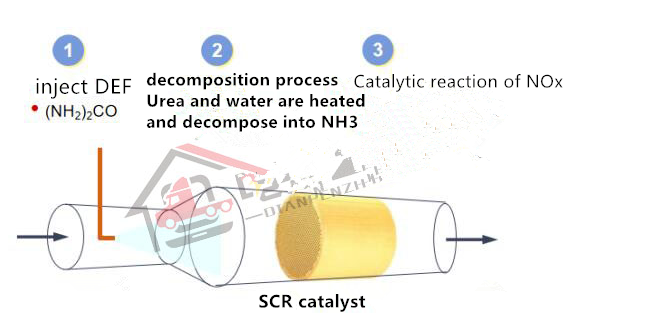
The SCR system converts nitrogen oxides (NOx) in the engine exhaust into nitrogen and water.
This reaction requires injecting diesel engine exhaust treatment fluid DEF (a nitrogen compound that is easily decomposed into ammonia) into the exhaust, which is injected into the exhaust upstream of the catalytic converter by a precise feeding device. The amount of DEF injected is controlled by the engine ECU. Ammonia reacts with nitrogen oxides (NOx) in a catalytic converter, producing harmless nitrogen (N2) and water (H2O)
2: Who monitors the SCR conversion efficiency, and how is the SCR conversion efficiency calculated?
1. Monitoring of SCR conversion efficiency:
There are two nitrogen oxygen sensors in the post-treatment system of National VI, and the front nitrogen oxygen sensor is installed between the turbocharger exhaust outlet and the DOC (oxidation catalyst) pipeline connection.
Front nitrogen oxygen sensor: measures the nitrogen oxygen concentration before SCR. Compared with the national fifth stage, the original exhaust replaces the model value and transmits the corresponding signal to the ECU for controlling the urea injection amount.
The rear nitrogen oxygen sensor is installed at the end of the exhaust pipeline to measure the NOx concentration after SCR for OBD monitoring, monitor the conversion efficiency of post-treatment, and achieve closed-loop control of urea injection.
The application of two nitrogen oxygen sensors can achieve closed-loop control of urea injection and accurately control the amount of urea injection.
