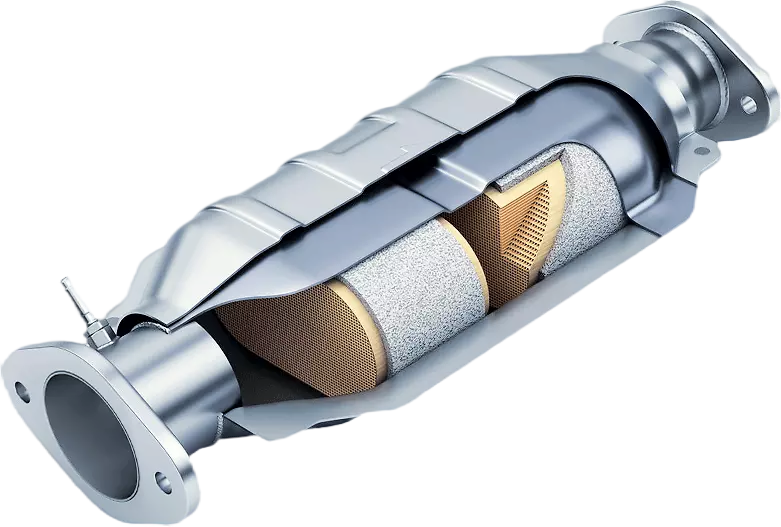
The structure and common fault analysis of three-way catalytic converter
catalytic converter
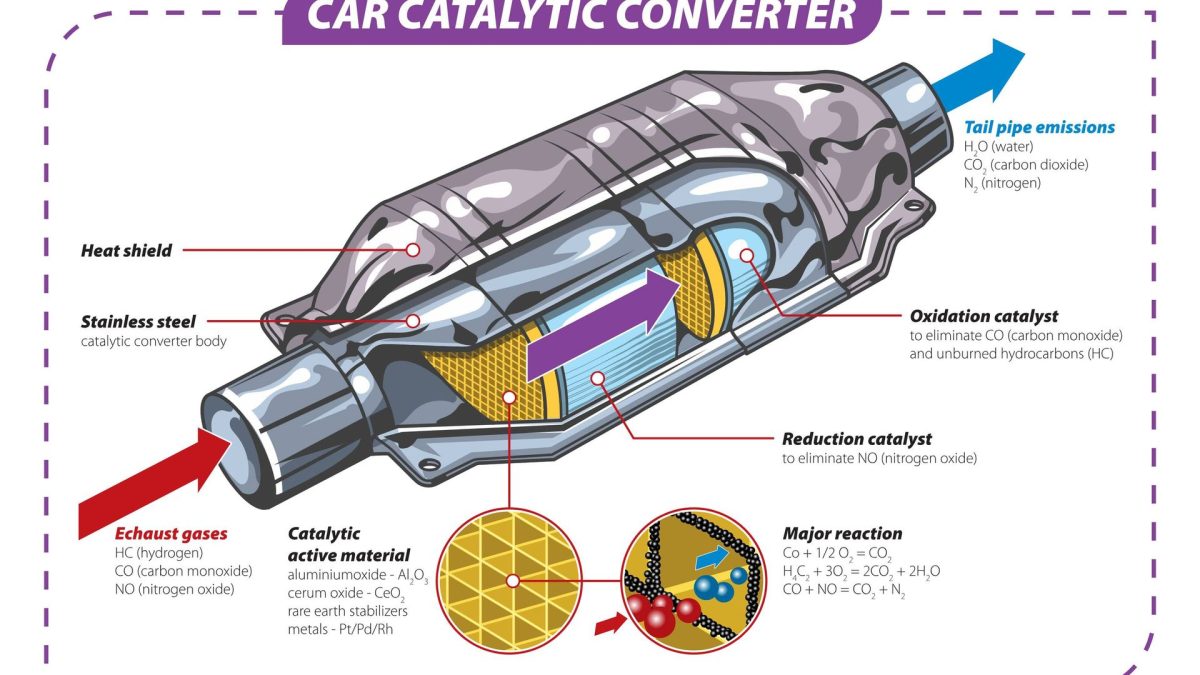
The three-way catalytic converter is a honeycomb structure made of ceramic material, which is filled with precious metals (such as platinum, rhodium, palladium, etc.) as catalysts. The working principle of the three-way catalytic converter is: when the high-temperature automobile exhaust passes through the purification device, the filter device in the three-way catalytic converter will enhance the activity of the three gases CO, HC and NOx, prompting them to undergo a reduction chemical reaction, in which CO is oxidized to become colorless and non-toxic carbon dioxide gas at high temperature; HC compounds are oxidized to water and carbon dioxide at high temperature, and NOx is reduced to nitrogen and oxygen.
The three harmful gases become harmless gases, so that the automobile exhaust can be purified. In other words, when the exhaust gas discharged by the engine passes through the three-way catalytic converter, the harmful gases in the exhaust gas (such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, nitrogen oxides, etc.) undergo oxidation-reduction reactions under the action of the catalyst and are eventually converted into harmless substances (such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, nitrogen, etc.).
Therefore, this three-way catalytic converter is a key link in the automobile emission system. If the three-way catalytic converter is damaged or aged, it will directly lead to the failure of the vehicle exhaust gas, and the vehicle will not be able to pass the annual inspection normally during the normal annual inspection. Regular maintenance of the three-way catalytic converter is also very important. Carbon deposits need to be cleaned and the engine oil replaced on time.
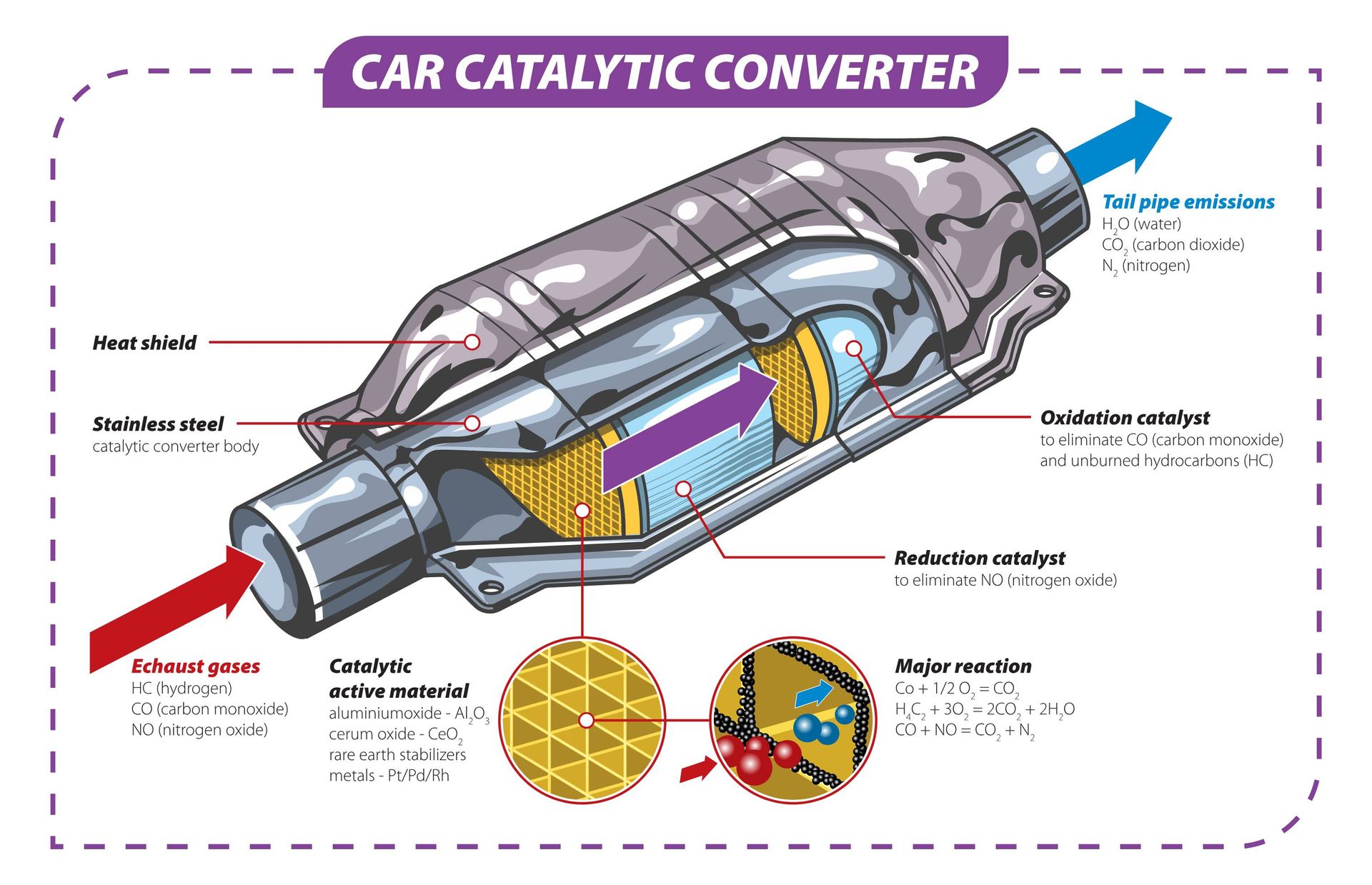
The role of three-way catalytic converter
- Reduce noise: The three-way catalytic converter can reduce the noise of engine exhaust and improve driving comfort.
- Protect the engine: The three-way catalytic converter can protect the engine from the corrosion of harmful substances such as sulfide in the exhaust gas and extend the service life of the engine.
- Improve fuel economy: By improving the combustion efficiency of fuel, the three-way catalytic converter can reduce exhaust emissions, thereby improving fuel economy.
- Purify exhaust gas: The three-way catalytic converter can effectively convert harmful substances in exhaust gas into harmless substances, reducing air pollution.

Reasons why vehicles need three-way catalytic converters
- Fuel economy: With the continuous rise in oil prices, fuel economy has become the focus of consumers. The three-way catalytic converter can improve the combustion efficiency of fuel and reduce exhaust emissions, thereby improving fuel economy.
- Environmental protection requirements: With the improvement of people’s awareness of environmental protection, governments of various countries have strengthened restrictions on automobile exhaust emissions. Vehicles must be equipped with a three-way catalytic converter to reduce the emission of harmful substances in exhaust gas and meet environmental protection requirements.
- Engine protection: Harmful substances in exhaust gas can cause corrosion and wear to the engine and shorten the service life of the engine. The three-way catalytic converter can convert harmful substances in exhaust gas into harmless substances to protect the engine from damage.
- Driving comfort: The vehicle will generate noise and vibration during driving, affecting driving comfort. The three-way catalytic converter can reduce the noise and vibration of engine exhaust and improve driving comfort.

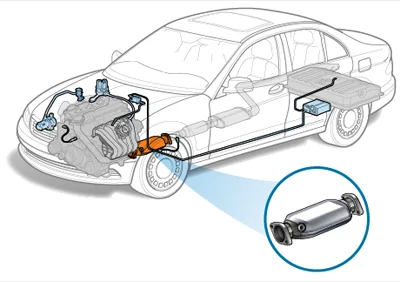
Installation position of three-way catalytic converter
The three-way catalytic converter is usually installed at the rear of the vehicle exhaust system, close to the engine. Its installation position ensures that the exhaust gas is fully heated before entering the three-way catalytic converter, thereby increasing the activity of the catalyst. At the same time, the installation position of the three-way catalytic converter can also prevent particulate matter in the exhaust gas from directly impacting the catalyst, thereby extending the service life of the catalyst.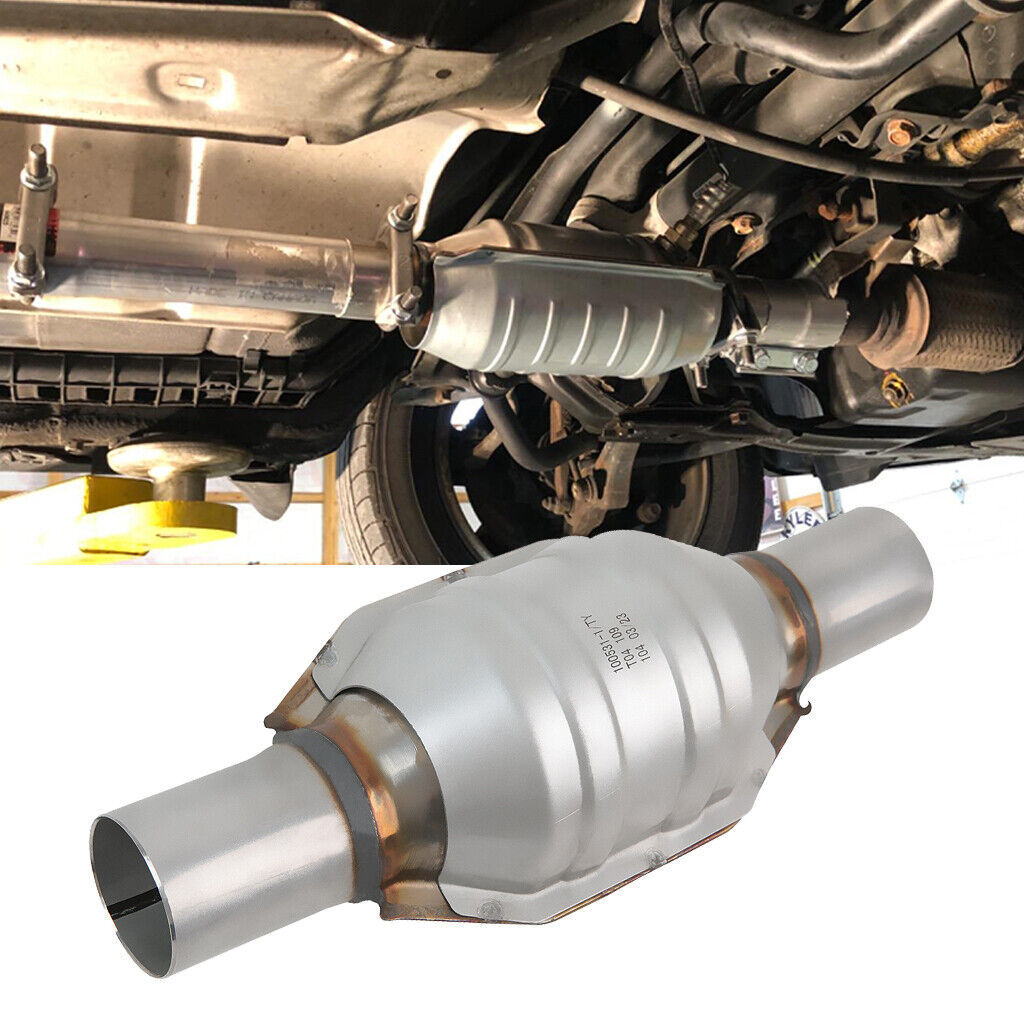
The failure types of three-way catalytic converters mainly include: failure, blockage, and breakage.
1. Diagnosis of failure failure The failure symptoms of three-way catalytic converter failure are excessive exhaust emissions.
There are three main methods for diagnosing three-way catalytic converter failure:
① Front/rear oxygen sensor signal comparison method .The front/rear oxygen sensor signal comparison method is a common method of using a special diagnostic instrument or a special oscilloscope to compare the signal voltages of the front and rear oxygen sensors to determine whether the three-way catalytic converter has failed.
② Inlet/outlet temperature comparison method .As shown in the figure below, at the working temperature, use an infrared thermometer to measure the inlet and outlet temperatures of the three-way catalytic converter respectively. The outlet temperature should be at least 10% higher than the inlet temperature.
③ Exhaust gas analyzer efficiency test method .◆ Repeated refueling test After the engine warms up and enters closed-loop control, the throttle is suddenly opened continuously in neutral, and the oxygen reading is observed using an exhaust gas analyzer: the oxygen reading remains below 1.2%, indicating that the three-way catalytic converter is working normally; the oxygen reading reaches 1.2%, indicating that the three-way catalytic converter is inefficient; if the oxygen reading exceeds 1.2%, it means that the three-way catalytic converter is not working.
◆ Oxygen content test After the engine is warmed up and enters closed-loop control, use an exhaust gas analyzer to check O2 and CO emissions:
If O2 is zero, repeated refueling tests should be performed;
if O2 is greater than zero, check CO emissions;
if CO emissions are greater than zero, it indicates that the three-way catalytic converter is not working properly.
2. Diagnosis of blockage fault The figure below shows the blockage state of the three-way catalytic converter.
When the three-way catalytic converter is blocked, the main fault symptoms are:
◆ When the blockage is serious, the engine cannot start;
◆ When the engine is misfired, the exhaust gas is more uniform and there is no “thumping” misfire sound;
◆ Acceleration is weak, and it is difficult to increase the engine speed and vehicle speed;
◆ Increased fuel consumption;
◆ Automatic transmission vehicles are forced to downshift frequently, etc.
There are three main methods for diagnosing the blockage of the three-way catalytic converter:
① Verify the fault phenomenon Using manual experience, observe and test whether the vehicle has obvious symptoms of three-way catalytic converter blockage. For details, please refer to the fault symptoms of the three-way catalytic converter.
② Check the exhaust back pressure with a vacuum gauge
③ Check the exhaust back pressure with a pressure gauge
◆ Connect the vacuum gauge to the engine intake manifold;
◆ Run the engine, and the speed is stable in the range of 2000~2500r/min;
◆ Keep the engine speed constant and observe the vacuum gauge reading;
◆ If the vacuum degree gradually decreases (absolute pressure increases), it means that the exhaust is blocked.
◆Remove the front oxygen sensor and connect the pressure gauge to the seat hole of the front oxygen sensor to ensure that the connection is well sealed;
◆Start and run the engine;
◆When the engine is at normal idling speed, the exhaust back pressure should be lower than 10kPa; when the speed is 2500r/min, the exhaust back pressure should be lower than 15kPa.
3. Diagnosis of broken faults The broken three-way catalytic converter is shown in the figure below. When the three-way catalytic converter is blocked, the main fault symptoms it presents are:
◆The shell is dented and deformed;
◆When the shell is knocked or the engine is accelerated or decelerated, a “clattering” sound is emitted from the inside;
◆Symptoms similar to blockage. There are two main methods for diagnosing the broken three-way catalytic converter fault: observation and listening. Through observation, confirm whether the three-way catalytic converter has collided and deformed; by knocking on the shell or accelerating or decelerating the engine, listen to whether the three-way catalytic converter emits a “clattering” sound to determine whether it is broken. Note: The three-way catalytic converter is usually replaced after the vehicle has traveled 80,000 km; the three-way catalytic converter should be replaced in the form of an assembly; the original parts that are the same as the original vehicle must be replaced.
Maintenance methods
- Regular inspection: Check the appearance and performance of the three-way catalytic converter regularly to ensure its normal operation. If the three-way catalytic converter is found to be damaged or aged, it should be replaced in time.
- Cleaning: We recommend that you can use AVL three-way catalytic cleaner for regular cleaning. Regular cleaning of the three-way catalytic converter can remove carbon deposits and impurities and keep it in good working condition. When cleaning, you should pay attention to using the correct cleaning agent and cleaning method to avoid damage to the three-way catalytic converter.
- Replace the catalyst: The catalyst is the core component of the three-way catalytic converter and its service life is limited. When the catalyst fails, a new catalyst should be replaced in time to ensure the normal operation of the three-way catalytic converter.
- Avoid using inferior fuel: Harmful substances such as sulfides in inferior fuel can damage the three-way catalytic converter. Therefore, you should avoid using inferior fuel during driving to protect the normal operation of the three-way catalytic converter.
- Avoid long-term high-temperature operation: Long-term high-temperature operation will cause the internal temperature of the three-way catalytic converter to be too high, accelerating the aging and failure of the catalyst. Therefore, long-term high-temperature operation should be avoided during driving to extend the service life of the three-way catalytic converter.